<< Back to Step 6
In step 7, we are seeing adding of Fixed Wavelength type add/drop multiplexers (ADM’s), to enable a scheme, which could offer not just simple point to point path, but also add/drop possibilities in middle nodes to extract tributaries and insert them back in main path.
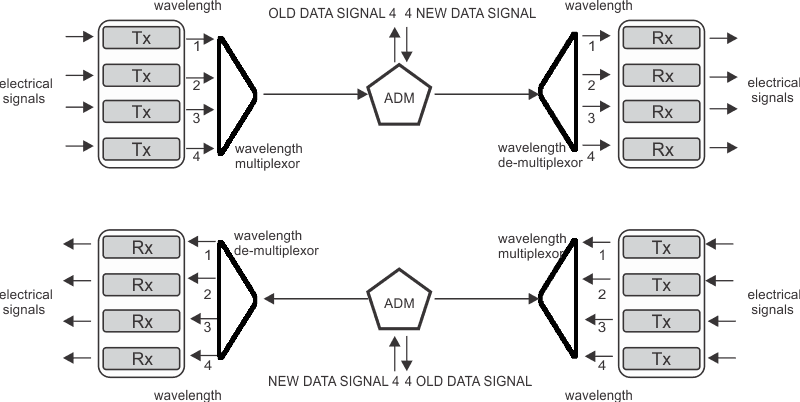
Figure 1: Example of middle add/drop node using OADM
However, as it was mentioned in previous steps, planning of such optical transmission pathes is not easy, as you still can’t predict how much of future bandwidth you will need.
Good example of ADM’s are SDH systems, where you can add/drop E1’s, V.35. Ethernet or other payload, make ring or daisy chain networks.
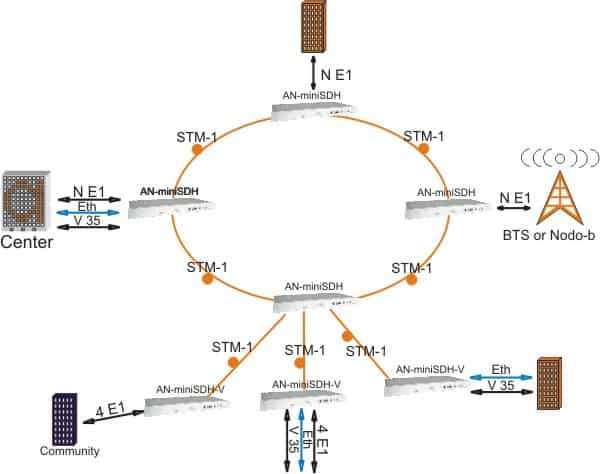
Figure 2: ADD/DROP scheme based on SDH STM-1 optical path using miniSDH system
This is also the main difference between SDH and PDH systems, (at least that moment of the history), when PDH could offer only point to point schemes without add/drop possibilities, while SDH could offer this.
To illustrate the importance of adding OADM concept, just compare for example this scheme:
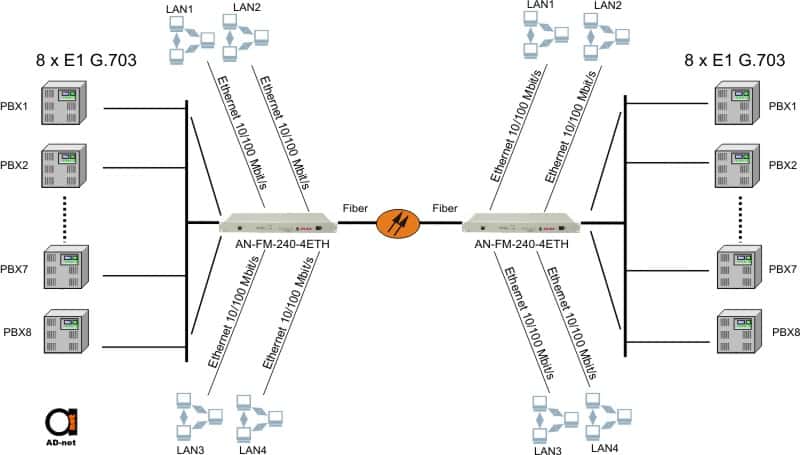
Figure 3: 8E1’s G.703 + 4 Ethernet using PDH multiplexer, point to point scenario
With the OADM SDH scheme in Figure 2. We can see that we can do much more flexible design in adding optical nodes in between to drop out tributaries.


