Let us summarize what we know about PON so far:
-
Using single feeder fiber line;
-
Using inexpensive optical splitters;
-
Employ point to multipoint architecture;
-
Downstream signal is being transmitted to every user. Only data intended for this user is being accepted;
-
Upstream traffic is point to point using TDMA.
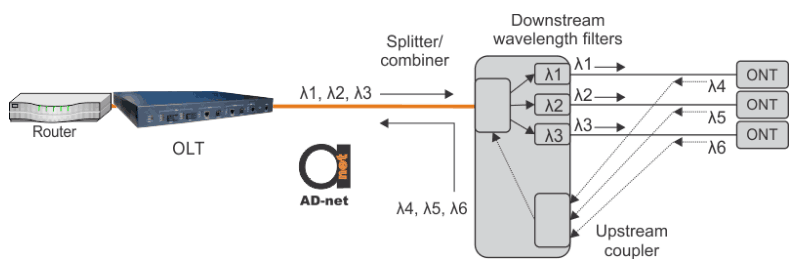
Figure 1. Passive unicasting using distinct wavelengths for different ONU’s.
Topologies
As defined before, PON is employing P2MP which supports a logical tree architecture. Although, it is possible to use logical P2P in PON for downstream by using multiple wavelengths. Figure 1 shows that it is possible to use passive wavelength filters to restrict data that that is not intended for group of users/single user. At the same time, Figure 1 introduces alternative for TDMA in the upstream direction. It is possible to use same wavelengths for upstream, as well as new wavelengths. If the same wavelengths are used – the downstream signal may be used for upstream data as a carrier wave. Modulation can separate signals.
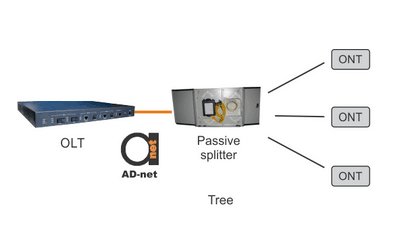
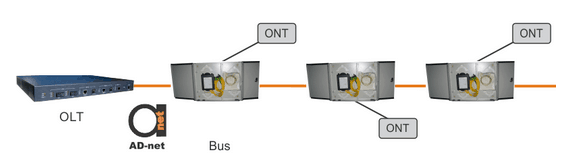
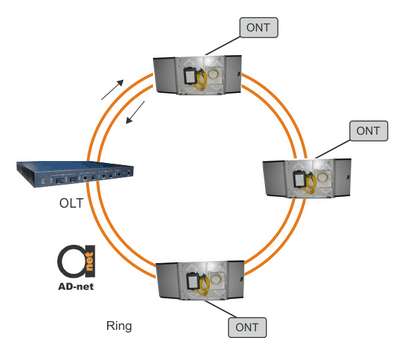
Figure 2. Tree, bus, and ring topologies.
Figure 2 is demonstrating three main topologies that are used in PON networks. In the tree topology, which is used for closely allocated subscribers, splitter is evenly distributing signal to ONTs/ONUs that are located relatively near from OLT.
Bus topology is extending spacing between ONTs, and is usually used for rural areas with large distances between subscribers.
Ring topology is the extension of the bus topology. It has two trunk fibers that are used to back up each other in the case of some of the network components failure.
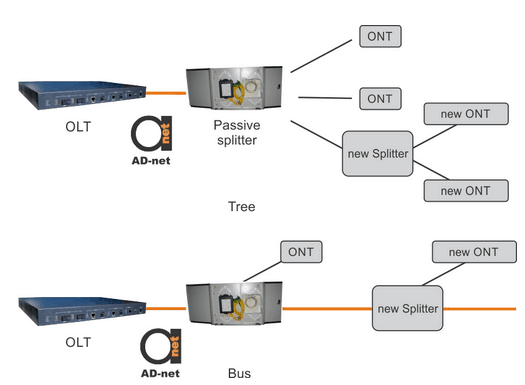
Figure 3. Adding new ONU to PON.
.All the topologies are supporting adding new ONUs to the network as shown in Figure 3. Tree topology can even accommodate sub-topology if necessary, while bus/ring topology just adds new subscribers with a new splitter.
PON can be used for short and long distances while maintaining high speeds and bandwidth. It supports a 100 km long network with up to 1000 users while transmitting data with rate of 1 Gbps per user.


