What is Optical Network? It is a network containing both active and passive elements. Active elements are in Central Office, at customer, in repeaters, switches and etc. All that equipment add cost and complexity to the network. What can be done instead? Passive Optical Network (PON) which had no active components between CO and customer. Passive equipment has no electrical power needs, it guides the traffic signals contained within specific optical wavelengths. Voice, video and data traffic flows (triple play) can be easily implemented using different wavelengths. And particular equipment used is GPON – GPON equipment.
In PON there is no active optical elements at any intermediate points along the network path.
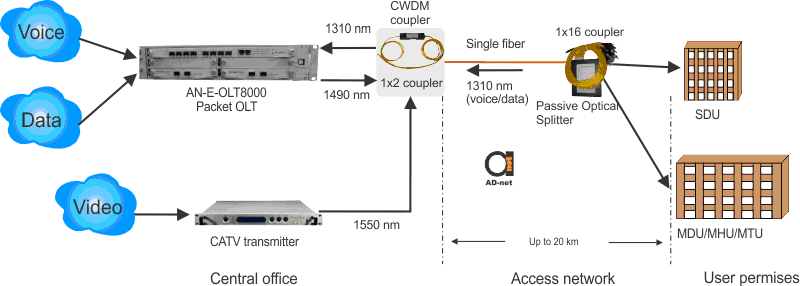
Typical PON, where central office equipment is connected with multiple subscribers using fiber optic network is shown in Figure 1. Central office could contain multiple equipment, such as public switched telephone network switches (PSTN), Ethernet switches, asynchronous transfer mode switches (ATM), IP routers, video-on-demand servers, backup storage systems (high capacity disk arrays and tape-drive libraries).
Passive optical power splitter is allocated near a building (housing complex, apartment or office building, a business park or other campus environment), and is connected to central office using one single-mode optical fiber wire.For the use of subscribers, signal is divided into N paths using splitting device. The power level for each subscriber can be easily calculated, dividing the optical power entering the splitter(P) by number of paths(N). Multiple splitters could be implemented in the specific path (possibly having different splitting ratios). Path can be splitted up to 64 paths, each of them would have individual single-mode fiber, running to each building or serving equipment. In PON, distance from central office to the customer could be up to 20 km, while having active devices only in central office and end terminal.
Active modules in the network can be divided in two main groups: OLT (Optical Line Terminal) located in central office and ONT (Optical Network Terminal) or ONU (Optical Network Unit) at the far end of the network. ONT is just connected directly to customer premises. ONU is allocated somewhere near cluster of homes or business (usually in telecommunication cabinet). ONU is connected to the premises by any twisted-pair wire, such as telephone lines or digital subscriber links or coaxial cable. Those are main components of GPON equipment based network.
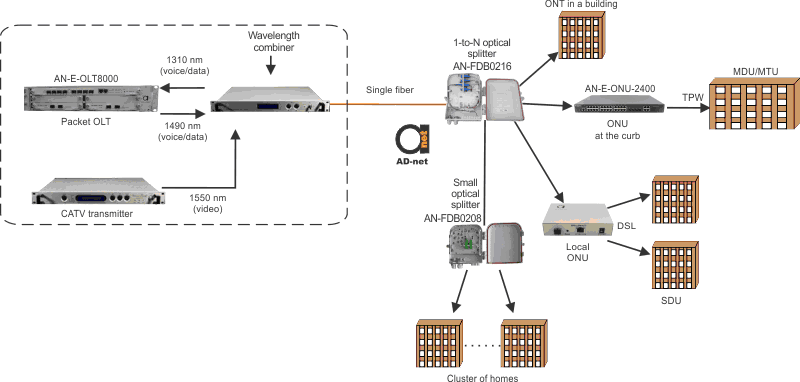
Sometimes it is more convenient and cheaper to put a single-fiber line from main splitter to distant localized cluster of homes or small business or within a centralized location in the neighborhood. In figure, a small optical splitter is located near the users’ houses, having one single-fiber line as input and multiple lines as output. Comparing to the long fiber link to each user form the main splitter, this type of network costs much less. ODN (Optical Distribution Network) is a collection of fibers, passive equipment and couplers that are allocated between the OLT and ONTs and ONUs.
Feeder cable is a link connecting central office and the optical splitter, which can split signal up to 32 subscribers. Optical splitter is allocated in 10 km from central office and 1 km from the subscribers. Multiple distribution cables are connected directly to users or to the access terminal (local splice box). Access terminal is connected to users using individual drop cables.
You maybe want take a further look at AD-net GPON equipment range.


