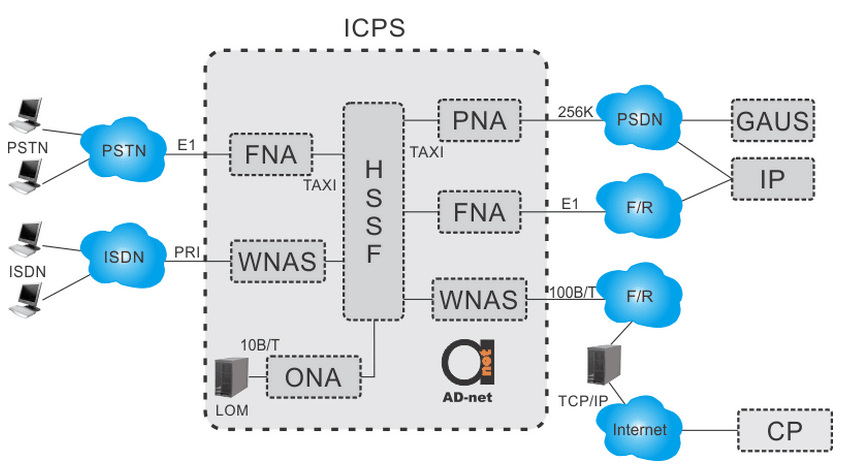
By the end of 90s, many telecommunication companies were offering “014xx” services, using public switches and Integrated Communication Process System (ICPS). ICPS network architecture is illustrated on the Figure 1. The “014xx” service was a phone number, that customers were dialing up and were connected to the corresponding modem bank of ICPS TNA. Next step in the service was the establishment of the session to frame relay or packet networks, and connection through PNA to the specific computer. However, modems could deliver only 56 Kbps, which was pretty slow for the growing Internet.
At that point in time, many companies were choosing between the ISDN and ADSL. Hybrid-fiber-coax (HFC) networks were not considered due the maintenance problems and ingress noise.
Telecommunication companies were splitting: R&D team was pushing ADSL as the solution for the fast and reliable network. Drawback of ADSL was cost, which was expected to be $1200 USD per subscriber. Financial team could not agree with huge costs and speed that was doubt that there are any services or applications requiring it. However everything changed fast, in 1998. Smaller telecommunication companies started offering broadband access service using cable modems over HFC following by ADSL solution. By that time, there were millions subscribers, demanding to be connected. Companies were adopting a flat rate of <$30 USD per customer which was giving significant savings for the subscribers. Larger companies were changing their strategies quickly to adopt new broadband solution.


