Networking installation consists not only from obvious components like cables and network cards. It is important to understand that network structure also includes telecommunication rooms, pathways, and spaces for cabling.
Let’s start with the horizontal and backbone cables. If the one would assume that horizontal cables are the cables that are located horizontally, the one is wrong. Name has nothing to do with the orientation of the cable. It refers to a cable located between outlet next to work area and a cross-connect panel in a telecommunication room. Horizontal cables are typically four-pair, unshielded twisted-pair of copper cables. In situations when there is high electromagnetic interference in the area, or security is critical, optical fiber might be used for horizontal cabling.
Backbone (vertical) cable is connecting telecommunications rooms to each other through the main cross-connect point of the building. Backbone cable might be copper (UTP, ScTP, or STP) or optical, depending on the network requirements. However, optical cable is preferred mean due to larger transmission distances.
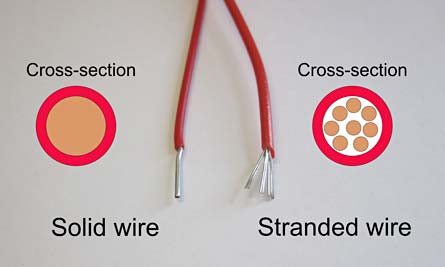
In order to connect workstation to the network, patch cables or patch cords are used. The same kind cables is used for connecting field-terminated horizontal cables and the networking equipment. This type of cable is using copper. Unlike horizontal UTP cables that use solid conductors, patch cords use more flexible stranded conductors.
Choice of the correct cable is difficult and decision is usually based on many requirements. Also, one must pay attention to the flammability factor of the cable, in order to secure the place in case of fire.


