Wall plates and connectors
Wall plates are the termination points for horizontal cabling near the workstation areas. They limit users interaction with horizontal cabling, providing convenient way of connecting to the network. These telecommunications outlets provide different interfaces based on the horizontal cabling and network requirements.
Cabling pathways
In order to route horizontal and backbone cables conduit might be used. Conduit is a metallic or nonmetallic pipe that cables go through. It is easy and simple solution that ensures cables convenient location. Choosing conduit, one should choose pipe with enough space for network growth. Typically the amount of cable space that is required should be 40% from the pipe size. It should not exceed 60%, otherwise this part of the network will not be future-proof.

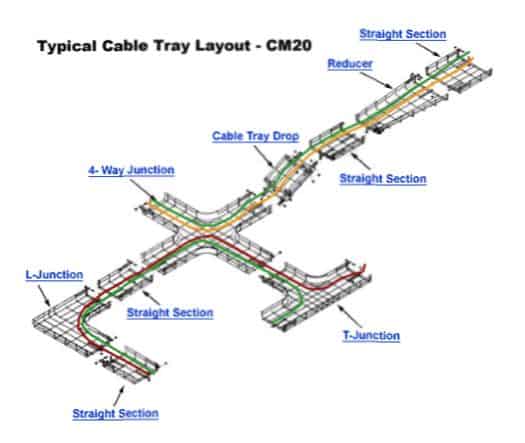
Cable tray is an alternative to the conduit. Unlike conduit, cable tray provides support for the cables while having no cover from top. That makes cables easily accessible, which is an advantage if troubleshooting or maintenance is necessary. This kind of system is typically running over the “fake ceiling”, ensuring that cables will not be located directly on the “fake ceiling”.
Raceway is commonly used conduit system that is used for surface-mounting horizontal cabling. These conduits are made of plastic and are installed on top of walls. It is common soution for the locations where in-wall or ceiling installation is difficult or not possible. Raceways are used for the copper cables, while fiber-protection systems are used for fiber.
Unlike copper, fiber cable has very low tolerance to the bending. Severe bendings result in cable partial or full failure. This why fiber-protection systems use rounded surfaces and corners. Since optic cable installation is a complicated task requiring proper training, it is important that fiber-protection systems would be installed by the professionals too. It should be noted that the cost of network deployment will be significantly higher compared to copper.


