Mainly there are three standards of PON. Table 1 is the extended version from previous article with ODN classes and transmission loss for them. Maximum amount of ONTs for a class depends on many variables like:
-
transmission loss;
-
fiber distance;
-
splitter;
-
optical power budget;
-
optical link penalty;
-
Tx launch power;
- Rx sensitivity
| BPON | GPON | EPON | XG-PON | |
| Downstream | 155.52 Mbps622.08 Mbps | 1.244 Gbps2.488 Gbps | 1 Gbps | 9.952 Gbps |
| Upstream | 155.52 Mbps622.08 Mbps | 155.52 Mbps622.08 Mbps1.244 Gbps
2.488 Gbps |
1 Gbps | 2.488 Gbps |
| Classes | ITU-T G.983B, C | ITU-T G.984A, B, C | IEEE 802.3ahPX10, PX20 | ITU-T G.987N1, N2, E1, E2 |
Table 2. Min/Max Loss of ODN Classes
| ODN Class | Min/Max Loss (dB) | ODN Class | MIN/Max Loss (dB) |
| A | 5/20 | E2 | 20/35 |
| B | 10/25 | PX10 | 5/20 |
| C | 15/30 | PX20 | 10/24 |
| N1 | 14/29 | P(R)X10 | 5/20 |
| N2 | 16/31 | P(R)X20 | 10/24 |
| E1 | 18/33 | P(R)X30 | 15/29 |
BPON was originated as asynchronous transfer mode passive optical network (APON). Since it implements ATM, it still being called sometimes as an asynchronous transfer mode PON. While being efficient and providing considerable QoS, ATM is having great overhead, have troubles with IP traffic accommodation and require conversion to the Ethernet for most users.
The standard for BPON is G.983.1. At first standard defined 155 Mbps for upstream and downstream, but later it was increased to 622 Mbps. Also standard defines:
-
powerful security features;
-
voice, data and video control functions;
-
adding new wavelengths for video broadcasting;
-
dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA)
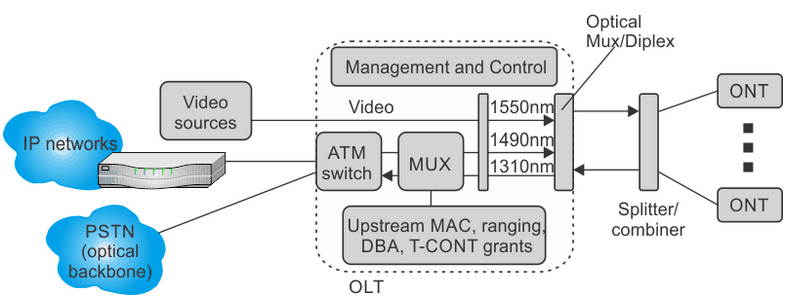
Figure 1.ATM-based BPON supporting triple play services.
Figure 1 shows main functions of ATM-based PON with addition of digital or analog video that is not mapped to the ATM stream.
GPON was being developed as larger scale, further distribution, higher split ratio and flexible in transmission formats PON. It supports ATM, Ethernet and TDM. Transmission rates are 2.4 Gbps and 1.2 Gbps downstream and upstream respectively.
Figure 1 shows main functions of ATM-based PON with addition of digital or analog video that is not mapped to the ATM stream.
GPON was being developed as larger scale, further distribution, higher split ratio and flexible in transmission formats PON. It supports ATM, Ethernet and TDM. Transmission rates are 2.4 Gbps and 1.2 Gbps downstream and upstream respectively.
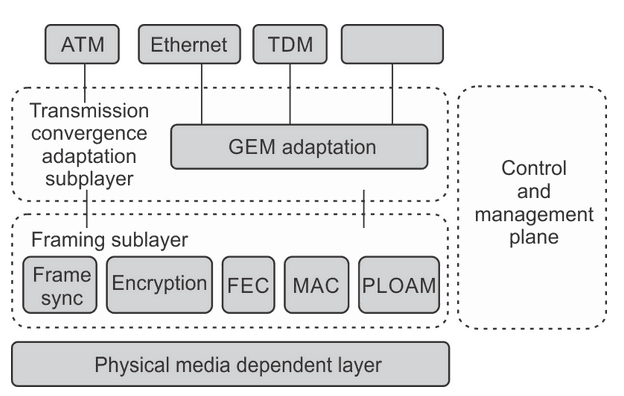
Figure 2. GPON protocol layers.
GPON encapsulation method called GEM is shown in Figure 2 together with GPON protocol layers.
Monitoring of existing ONU and registering new ones, configuring bandwidth, data encryption, forward error correction are included in the control and management plane. GPON management utilizes the ONT management control channel protocol and an ONU management information base (MIB). Standard ONT management and control interface and ONU/OLT. This allows communication between equipment from different manufacturers.
EPON was developed for Ethernet extending into subscriber access network. It uses frame formats and MACs supported by the Ethernet switches and other Ethernet equipment. It is using IEEE 802.3ah that is addressing physical and data link layers. It transmits 1 Gbps in each direction with wavelengths of 1490 nm downstream, 1310 nm upstream, and 1550 nm for video broadcasting. The EPON is shown in Figure 3.
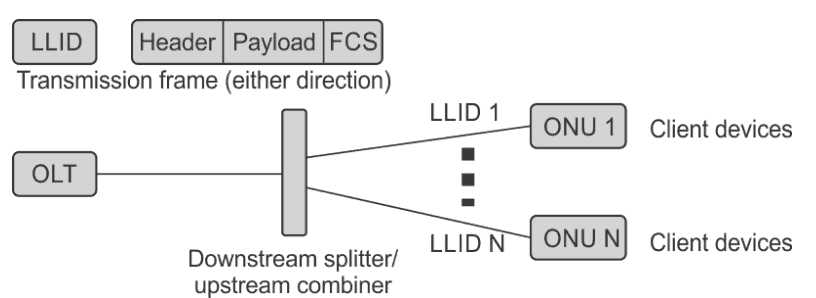
Figure 3. Simplified EPON with all services at an ONU.


