May
18
2012
Modern people are highly dependent from the network resources due the communications and work resources transmitted through it. Since physical cuts in a fiber transmission line can result in the system downtime, fault management is highly important and widely implemented.
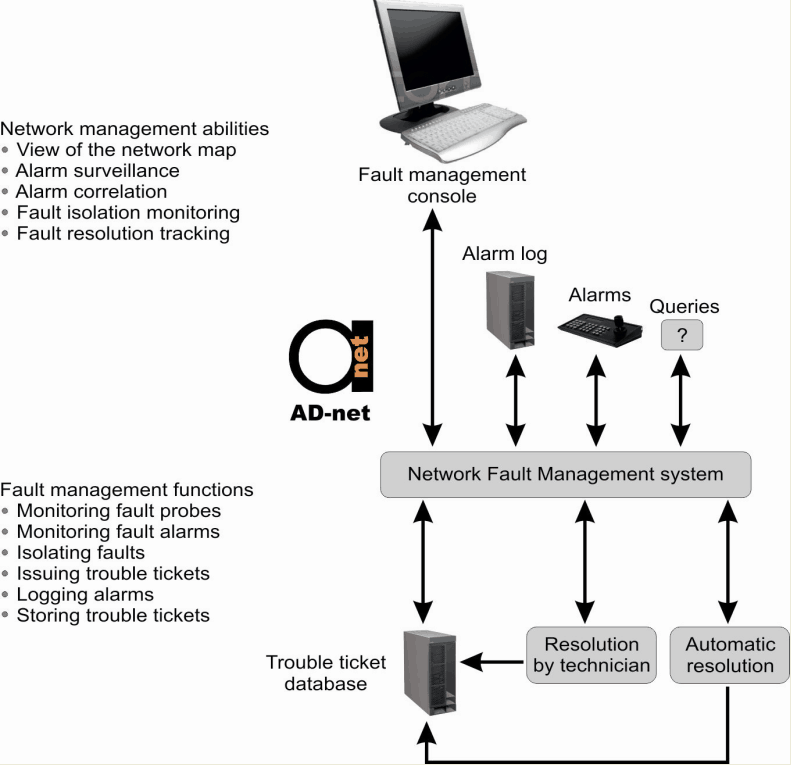
Figure 1. Fault management processes
- Alarm surveillance is a tool used to report alarms and possible sources of the alarm to the NMS. These alarms may differ due the different levels of security. All the unresolved alarms are stored in alarm log and can be easily retrieved from it by network manager.
- Fault-isolation is used to allocate the origin and possible cause of the error. It can be found manually by the network manager or automatically. Fault-isolation is having functions of diagnostic testing and alarm correlation.
- Trouble tickets are created by NMS after the fault isolation and are passed to a technician or to the automatic fault-correcting mechanism. Tickets are carrying information about the fault and possible solution. When the solution is corrected or approved the trouble ticket is stored in a database for further access.
- Operational testing is used when problem is solved to assure that everything works properly. The repair point is tested on all main subsystems and the results are recorded.
It is critical to have comprehensive maps of the network (physical and logical). These maps can give a view of th the network connectivity and the operational status of all equipment in the network on a display. This map allows constantly view the network, allocate error point and immediately do the corrective actions in the large PON network.
Products related to PON networks you can find here


