The delivery of high quality and highly reliable service requires enhancement of survivability and network protection. The ITU-T recommendation G.983.1 is including necessary criteria and protocols. So, if SDH and similar products have been offering 1+1 optical path protection, and ring scenarios, then how about those topics in FTTH – GEPON/GPON?
Let’s see what we can do here.

Figure 1. Basic FTTP network protection architecture. Type A.
In this type of protection (Figure 1), only optical fiber is protected by using spare feeder fiber. Some of the burden that is used for link reconfiguration is shifted to spared fiber. For example, when the malfunctioning fiber is switched to a protection fiber, the ranging procedure is needed to be done again, because optomechanical mechanism functions independent of any protocol.
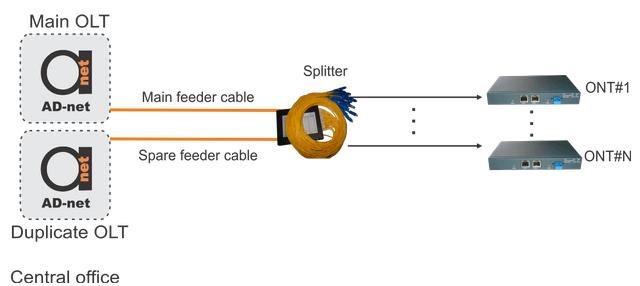
Figure 2. Basic FTTP network protection architecture. Type B.
In this type of protection (Figure 2), central office is having additional OLT equipment installed having spared fiber cable. If the first (primary) OLT is broken or its interface fails, the service is switched to the standby OLT and its link. The control of switchover is managed within the central office.
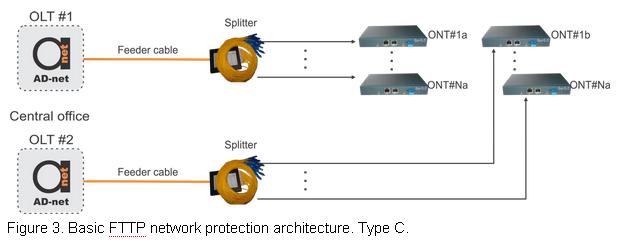
Figure 3. Basic FTTP network protection architecture. Type C.
In this design (Figure 3) there is fully operating backup PON network. Both networks are fully operating at the same time. Network fidelity is monitored constantly and if using of backup network is faster, network is switching to use it. In case when primary network is operating normally, receiving equipment selects signal from primary PON. This protection method is protecting from any kind of equipment or signal failure.
More about our GEPON PON models here.


