The ONT (Optical Network Termination) is the name for the home receiving equipment, also known as NID (Network Interface Device). Lets imagine the example system, where single fiber is used for carrying 1550 nm video signal and 1310 nm bi-directional data signal. Signal is being splitted to separate wavelengths by WDM (Wave Division Multiplexer). AGC is taking care of removing all RF level variations. In order to support RF return from STTs the RF diplexer is being used.
While processing 1310 nm data signals going to and from a digital optical transceiver, it supports the FTTH protocol and converts signals into standard analog phone lines and 10/100 Base-T connections. The RF diplexers routes the upstream signal to A/D (analog-to-digital) converter in order to support RF return from common cable TV STTs.
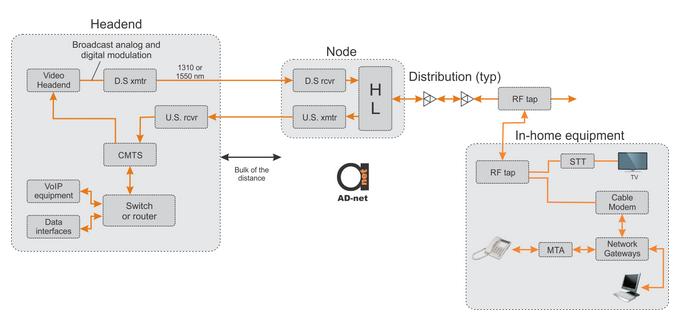
Figure 1. Example HFC network.
High-level view of an HFC network is visible on Figure 1 that shows compatibility of FTTH system with HFC system. Headend on the left side of the figure is having video headend that supplies signals for the downstream optical transmitter. Data and voice network interface is being handled by CMTS connected to switch or router. CMTSs, STT upstream control receivers, status monitoring systems or switched circuit voice systems are supplied with return signals by upstream optical receiver. Headend is connected to the HFC node and further through the amplifiers cascade. In the customers premises, the signal is being split and video data that goes to STT and cable modem that is further connected to switch or other gateway device. Further, multiple computers could be connected and the voice signal goes to the MTA (Media Terminal Adapter).
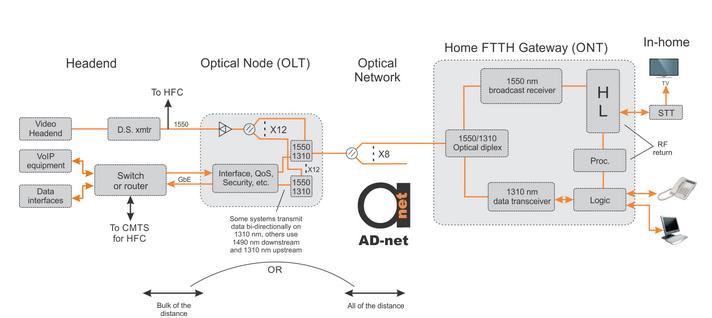
Figure 2. Example FTTH network.
Figure 2 shows the same scenario implemented with FTTH technology and similar interfaces. Video headend terminates on a downstream transmitter. Standard Gigabit Ethernet interfaces are connecting router that has been used for CMTS to the OLT. In the OLT the QoS and Security being added while data is being modulated onto a 1310 nm optical carrier. OLT might be allocated either on the headend or on some distance from it. If it is allocated remotely, the distance to subscriber could be longer. While powered by the same source that used for HFC gear, it could amplify the signal for longer distances. It would be allocated at cabinet or in strand mounting that could be in up to 70 km from the headend resulting in 90 km in total from subscriber to the headend.
If the OLT is allocated at the headend, the distance would be limited by only 20 km, but the network will be passive (PON – passive optical network) having no powered elements. The network between the home and the OLT is all passive as well having just dielectric fiber and optical taps.
FTTH gateway (ONT) is usually allocated on the side of the home, where optical diplexer is separating signal into the different paths with different wavelengths.


