Resource allocation, particular bandwidth allocation, and detection of unusual conditions or problems are included in management and control of the network. In the PON network management can be either centralized or distributed. Centralized system is preferable for convenient monitoring of the physical channel. In order to manage bandwidth allocation it is required to have connection with a functioning ONU.
PON is developed in a way that some parts of the subscriber line are shared between users. Although all the ONUs could receive data from OLT, upstream data goes from subscriber only to CO. Even though splitter and feeder fiber are common, data cannot be transmitted directly from one network user to another. It is a good security measure, but it also makes impossible for ONUs to detect data collision in the upstream direction.
Easy solution would be assigning fixed time slots for each ONU. This type of bandwidth allocation is called static bandwidth allocation (SBA). This is a possible solution for network with Constant Bit Rate (CBR) where traffic is constant. In real life situation some ONUs can be idle while others have great amount of data to transmit. But since idle ONU has defined time slot it will occupy the channel even with no data to transmit. This will create bottleneck for the network that makes SBA to be not preferred solution.
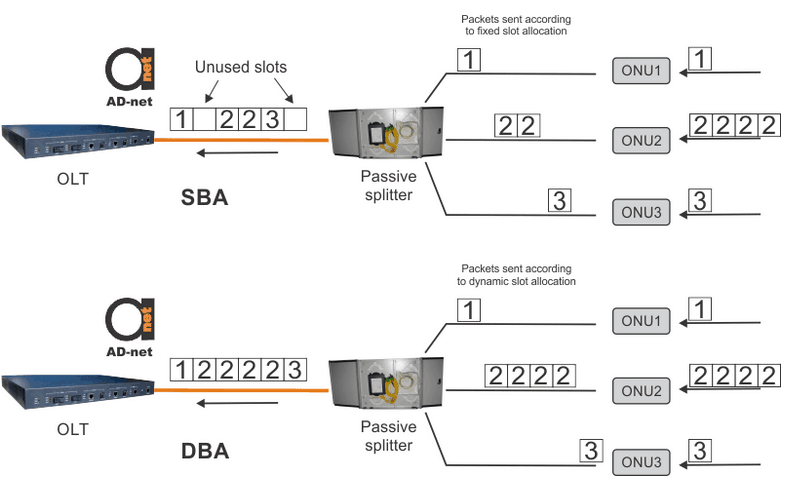
Figure 1. Static bandwidth allocation (SBA) and dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA).
Problem is solved with Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA). This solution is based on dynamic assigning of time slots based on ONUs requests. DBA is improving Bandwidth allocation compared to SBA as is is shown in Figure 1.


