Data center should have large amount of different security features, since different enterprises would have different security requirements. Security measures are necessary not only for clients data safety, but also for ensuring compliance with government and industry regulations. Dividing network into security zones is best practise for ensuring security. Some environments require physical separation of front-end and back-end traffic. However, converged environment can only provide logical traffic separation, which would be inappropriate for sensitive applications. It is considered secure to use separate VLANs for network traffic isolation, due to modern switch nonsusceptibility to VLAN-hopping technique.
Figure 1 shows that there is security exposure between aggregation and core layers in conventional network. It could face one of the following problems:
-
buffer overflow
-
cross-site scripting
-
spear phishing
-
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service)
-
URL tampering
-
SQL injection
Another risk of exposing data happens due to human error possibility. Flow-control standards allow to minimise risks.
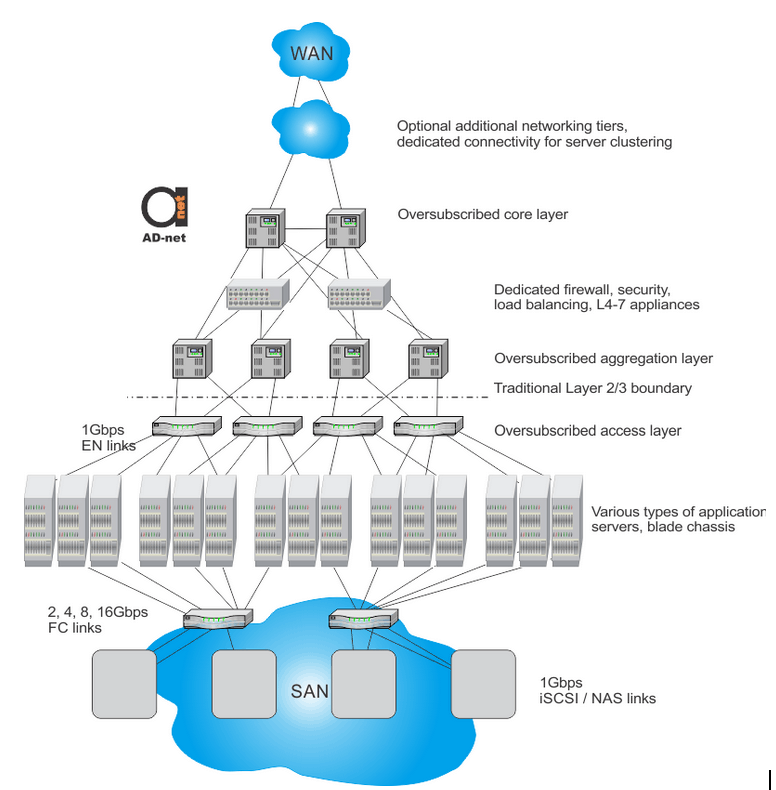
Figure 1. Design of a conventional multitier data center network
Since there are multiple different ways of breaching security, architecture could not concentrate on protecting from single type of threat. Following techniques could help to prevent intrusion to the network:
-
firewalls
-
access control lists
-
data encryption
-
deep packet inspection
-
zoning of storage networks
-
web filtering
-
segregated VLANs
-
traffic policing
-
Layer 2 authentication
-
endpoint integrity
-
network information
For the long range network, WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is recommended in order to detect physical layer intrusion, encrypt data, and isolate traffic using different wavelengths.


