PON system might have different types of problems happening in different parts of network. Location of the problem defines whether all or just several subscribers will affected. Troubleshooting allows to identify location and the source of the problem. The problem might be one of the following:
-
connector damage
-
connector misalignment
-
fiber break
-
fiber bend
-
power level problem for ONUs/ONTs
Problems will affect all the network users if it occurs in the shared part which include GPON OLT, feeder fiber, and splitter. If the problem occurs after the splitter, it will affect only customers that are downstream from the failure point. Figure 1 shows different zones that can be troubleshooted. Zones 1-3 are affecting whole network, while 4-5 are causing disturbances to a limited amount of customers. Table 1 shows possible problems and their locations.
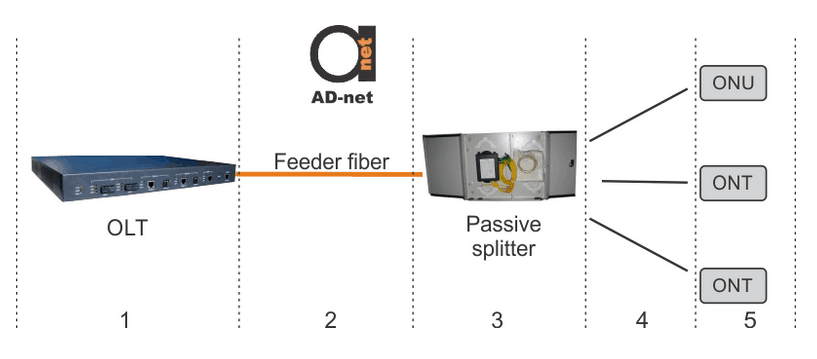
Figure 1. PON troubleshooting zones.
Troubleshooting is done using two main pieces of equipment (although, there are more solutions) – Optical Power Meters (OPMs) and Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDR). OPM is constructed of a solid-state detector, signal conditioning circuit, and digital display. It is mainly used for measurement of continuous light beams average power. It can operate in a wide range of optical powers and wavelengths. It is used as shown in Figure 2, where OPM is testing optical power while being connected to the distribution fiber.
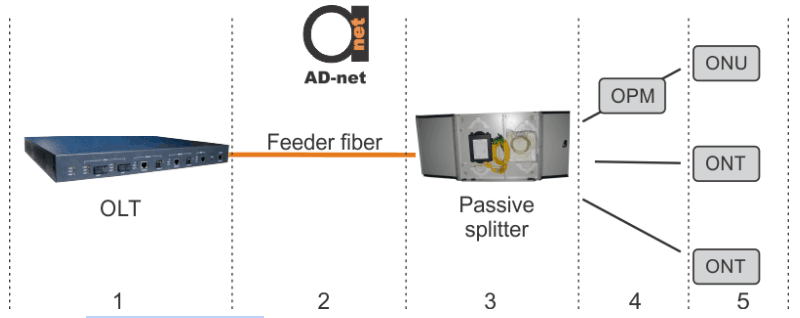
Figure 2. OPM troubleshooting
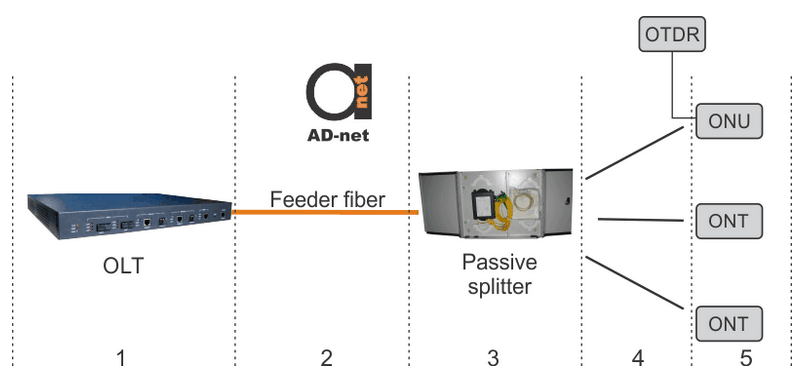
Figure 3. OTDR troubleshooting.
OTDR is connected in the PON as shown in Figure 3. It can measure distance to the break in the fiber or to its attenuation point by sending light pulses and extracting light reflection. Depending on time, intensity, and direction it can measure total fiber distance and its attenuation.
When troubleshooting, PON will return traces from multiple branches, which makes difficult to find problem if it is located in some particular branch. Isolating other branches, will help in troubleshooting. Branches could be isolated by using different wavelengths for different branches and by using different response times with selective use of ONU reflectors.


