Everyone’s or more or less familiar with a term “firewall”, and has more or less understanding what it is – why really, why firewall is used, and why firewall is important for modern networks?
Firewalls are used on networks to provide security boundaries between our inside network devices and untrusted areas like the Internet features such as access lists and security zones are used to block untrusted source traffic from entering your network.
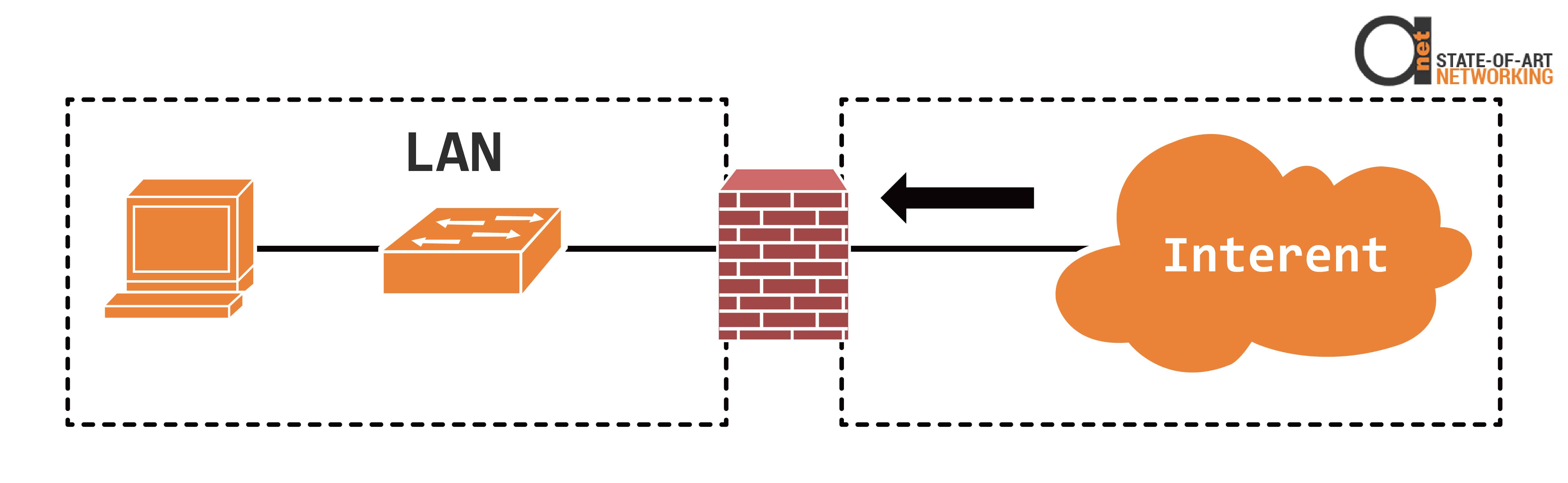
Figure 1: Local Area Network (LAN) is protected from Internet by means of firewall
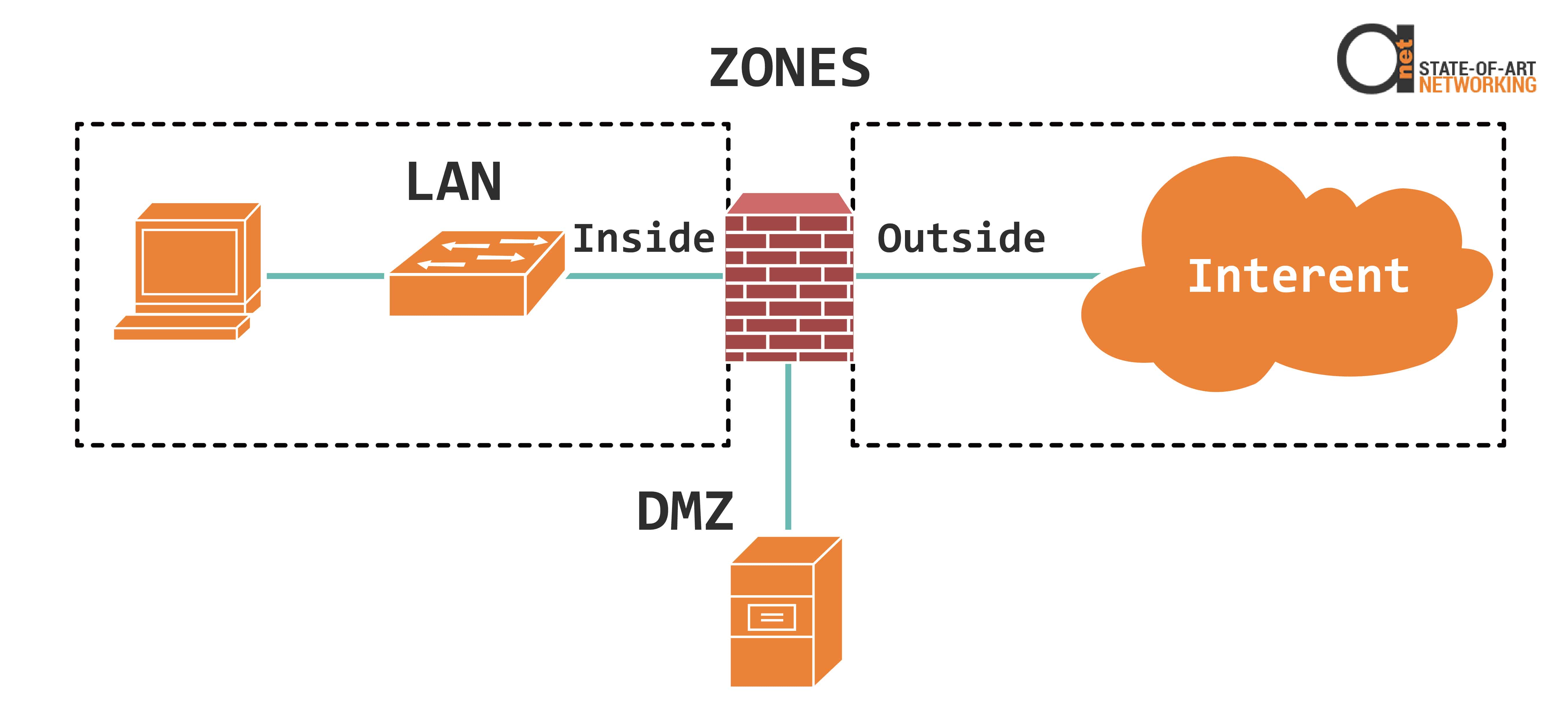
Figure 2: Inside, Outside and DMZ zones
Most networks have at least three zones:
- inside zone
- outside zone
- DMZ zone
Firewalls can monitor connection states between zones to know where connections are initiated from.
The goal is to only allow untrusted outside traffic through the firewall if the connection was initiated from the inside of the network and to not allow traffic through the firewall, if the untrusted traffic is initiated from outside of the network.
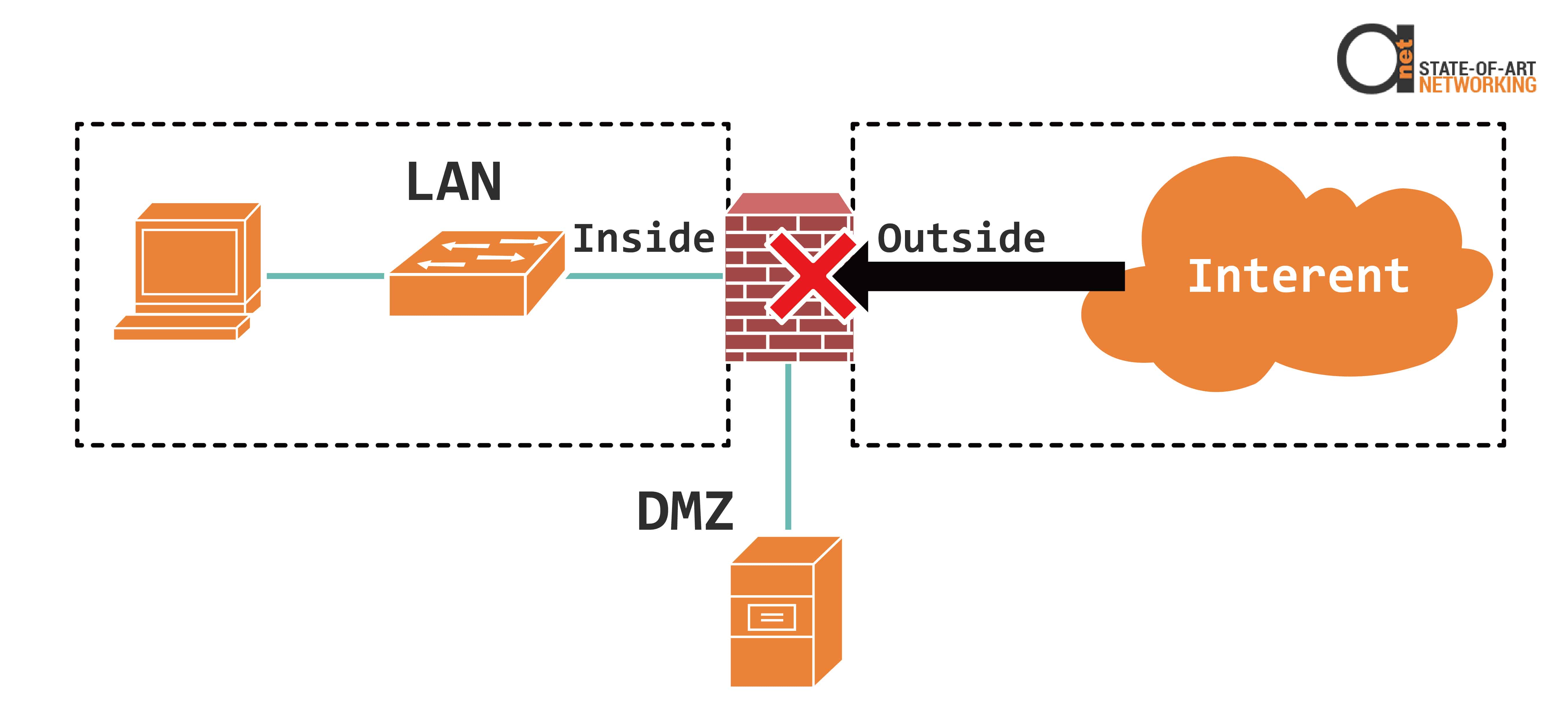
Figure 3: Firewall blocks untrusted traffic from outside getting into LAN network
For example, when you go to Google in your web browser, your home firewall knows that your pc started the connection and that it can allow Google responses to go through the firewall to your PC.
However, if Google tried to connect directly to your pc without you requesting any information than the firewall would block it. Now, there are also times when an outside network and the untrusted zone needs to initiate a connection to the internal network for services like web servers and email.
For devices that need to be accessed from the outside, there is a special firewall zone called a DMZ, which stands for a demilitarized zone, the firewall would be configured with ACL rules to allow specific IP and port destinations to connect from the outside to the DMZ.
For example, if your web server and needed to be access from the Internet, then you would connect it to the DMZ zone and configure an ACL entry to only allow traffic destined to the web servers, IP and TCP, port 80.
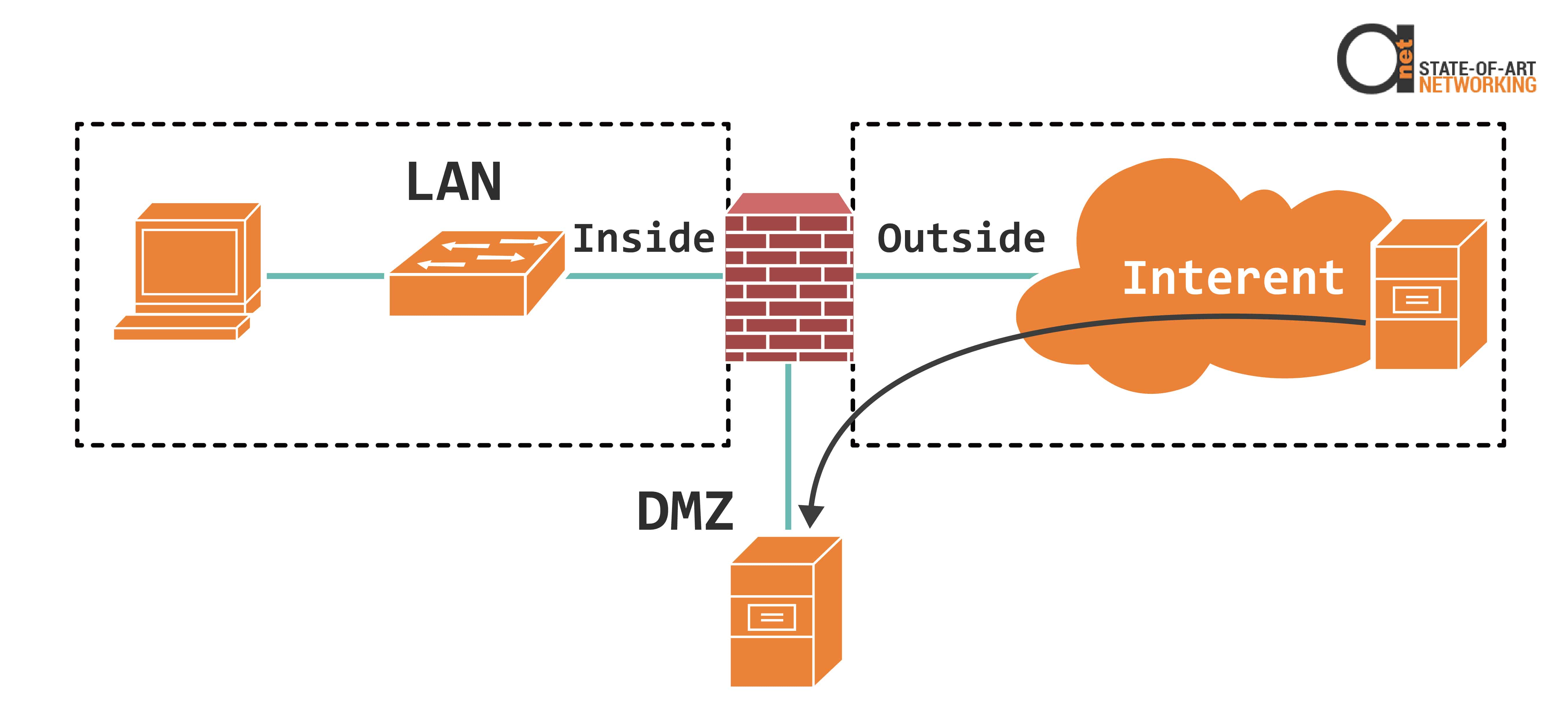
Figure 4: DMZ allows outside traffic come into webservers specified IP address
Another key role that our firewalls take on as NAT or Network Address Translation. Whenever we are accessing the internet or forwarding traffic inbound to a DMZ device, we need NAT to communicate to public IP’s on the Internet.


